Import
What is the Mediterranean diet?
A simple question, but with much deeper implications than one might imagine.
It's not just a way of eating. It's an entire philosophy of life that has its roots in the traditions of countries like Greece, Italy, and Spain.
Much more than a food list — it's a way of eating, enjoying, and living.
But why has it gained such a worldwide reputation? And what is the Mediterranean diet in the eyes of the scientific community?
Let's find out.
Global fame and recognition
In recent years, more and more doctors, nutritionists and scientists have been referring to the Mediterranean diet as one of the healthiest dietary patterns.
International organizations, such as the World Health Organization and UNESCO, have recognized it as cultural heritage.
And it's no coincidence. With dozens of studies proving its benefits, the Mediterranean diet has become a benchmark.
Article Objective: To present the key elements and benefits
In this article we will answer in detail the question "what is the Mediterranean diet?"
We will examine its historical origins, key characteristics, and documented health benefits.
And of course, we'll see how you can easily incorporate it into your daily life.
Origin of the Mediterranean Diet
Historical background
To understand what the Mediterranean diet is, we need to look back into the past.
This diet was shaped through centuries of traditional practices. With roots in the ancient Greeks, Romans, and peoples of the Mediterranean, it formed the foundation of everyday life.
The abundance of olive oil, vegetables, fish and cereals was a result of climate and geography.
Countries that represent it (Greece, Italy, Spain, etc.)
When we wonder what the Mediterranean diet is, the first countries that come to mind are Greece, Italy, and Spain.
Each of them has its own gastronomic identity, but they all share common principles.
Fresh, seasonal food, the use of olive oil, and sociability in eating are a common denominator.
Cultural significance
Beyond foods, what the Mediterranean diet is also touches on culture.
Food is associated with family, friends, celebrations. It is not just a nutritional need.
It's a way to get close to people.
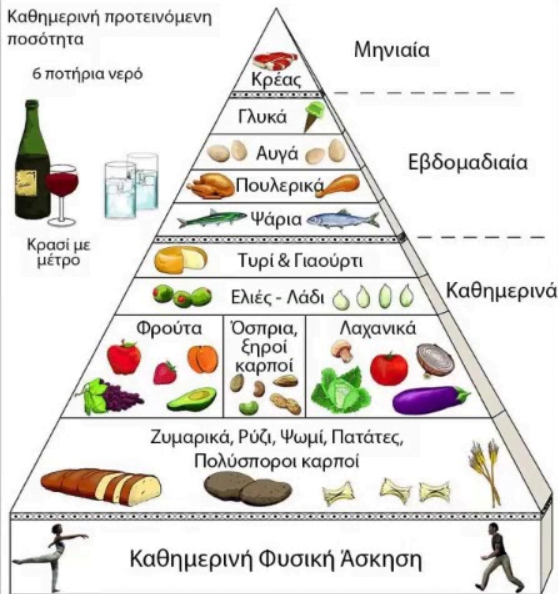
Key features of the Mediterranean Diet
Daily consumption of vegetables and fruits
If we want to understand what the Mediterranean diet is, the answer starts with fresh vegetables and fruits.
These form the basis of every meal.
Each dish is full of color, flavor and vitamins.
Emphasis on olive oil as the main source of fat
Olive oil is not just an ingredient. It is the king of Mediterranean cuisine.
Mediterranean diet without olive oil… it just doesn't make sense.
Rich in monounsaturated fats and antioxidants, it is the main source of fat.
Whole grains
The cereals, and especially whole grain products, play an important role.
Bread, pasta, barley cakes — sources of fiber that support intestinal health.
Legumes
Another foundation of what the Mediterranean diet is is the legumesLentils, beans, chickpeas.
Cheap, nutritious and tasty, they have a constant presence on the weekly menu.
Moderate consumption of dairy products (mainly yogurt and cheese)
Dairy products consumed in moderation.
Mainly yogurt and cheese, rich in probiotics and calcium.
Limited consumption of red meat
The Mediterranean diet teaches balance. Red meat is present, but in limited quantities.
Other protein sources are preferred.
Fish and seafood 2-3 times a week
The sea plays a role. Fish and seafood are a key part.
Rich in omega-3 fats, they enhance cardiovascular health.
Moderate wine consumption (mainly with meals)
Red wine, always in moderation and accompanied by food.
Common practices: eating in a social context, enjoying the meal
Finally, eating is a social experience. Meals with family, friends, without rushing.
This is an integral part of the Mediterranean diet.
Health benefits
Cardiovascular protection
One of the first benefits that studies show is heart protection.
The Mediterranean diet reduces the risk of heart disease.
Weight adjustment
What is the Mediterranean diet if not a balanced approach that helps maintain a normal weight?
No excesses, no deprivations.
Prevention of type 2 diabetes
Another important benefit is the reduction in the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. The variety of fiber and low glycemic load play an important role.
Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory action
The Mediterranean diet is directly related to the consumption of antioxidants. Fruits, vegetables, and olive oil protect against inflammation and premature aging.
Longevity
It is no coincidence that regions with longer-lived populations follow this dietary model.
The Mediterranean diet promotes longevity.
Wellness
This food also brings mental well-being.
Not only because of the nutrients but also the philosophy of the food itself.
The scientific documentation
Research and studies
Countless studies answer why you should choose the Mediterranean Diet.
And they all agree: it offers multiple health benefits.
Recognition by international organizations (e.g. UNESCO, WHO)
UNESCO has recognized it as an intangible cultural heritage.
The World Health Organization promotes it as a dietary standard.
How to incorporate the Mediterranean Diet into your daily life
Tips for small changes
Start with simple steps.
Add more vegetables to every meal.
Use olive oil instead of other fats.
Menu ideas
An example:
- Breakfast: yogurt with honey and walnuts.
- Lunch: lentils with olive oil and salad.
- Dinner: grilled fish with vegetables.
And that's how you learn what the Mediterranean diet is in practice.
Role of physical exercise and lifestyle
The Mediterranean diet is associated with movement.
Walks, hiking, active lifestyle.
It's a way of life, not just a menu.
Conclusion
Let's summarize: what is the Mediterranean diet?
- It is a dietary pattern full of flavor, nutritional value, and culture.
- It's not a diet.
- It's a way of life.
- With respect for food, enjoyment of food and love for life.
- If you want to adopt a healthier and more balanced diet, the Mediterranean diet is the ideal choice.
Get started today.
Your body — and your spirit — will thank you. Yes, the Mediterranean diet is a first-class choice.


